Abstract
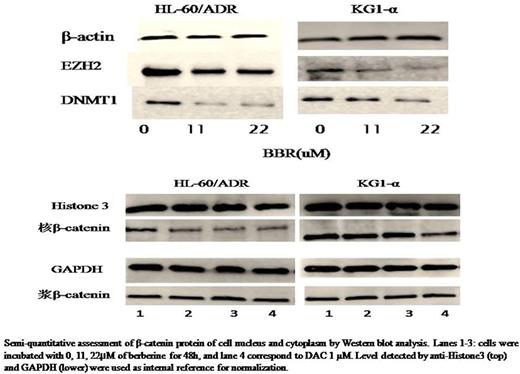
Berberine (BBR) has a wide range of biochemical and pharmacological effects. However, the exact mechanism of these bio-activities remains poorly understood. Based on the bioinformatics analyses, our study firstly discovered the possibility of berberine being an epigenetic modulator in U266 cells. We demonstrated significant similarity between berberine and two epigenetic modulators (CG-1521 and TSA). We conducted this study to explore how these molecular events are regulated by berberine in (Acute Myelocytic Leukemia) AML cells. The analysis found that enzymes involved in histone acetylation and methylation have been impacted predominantly. In addition to this, the results showed that berberine also inhibited the expression of EZH2 and DNMT1 in HL-60/ADR and KG1-α cells, both in protein and mRNA. In DNA methylation, BBR induced decrease methylation level in the SFRPs, then depressed the wnt/β-catenin pathway.The results of this study suggest that berberine might modulate expression of epigenetic regulators importent for some downstream pathways, thereby manifests its various bio-activities in AML cells.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal